New Delhi: Recognising privacy as a fundamental right, a draft personal data protection bill Friday proposed “explicit consent” for processing ‘sensitive personal information’ like religious or political belief, sexual orientation and biometric information.
It also provided for the right to be forgotten and prescribed steep penalties for violations.
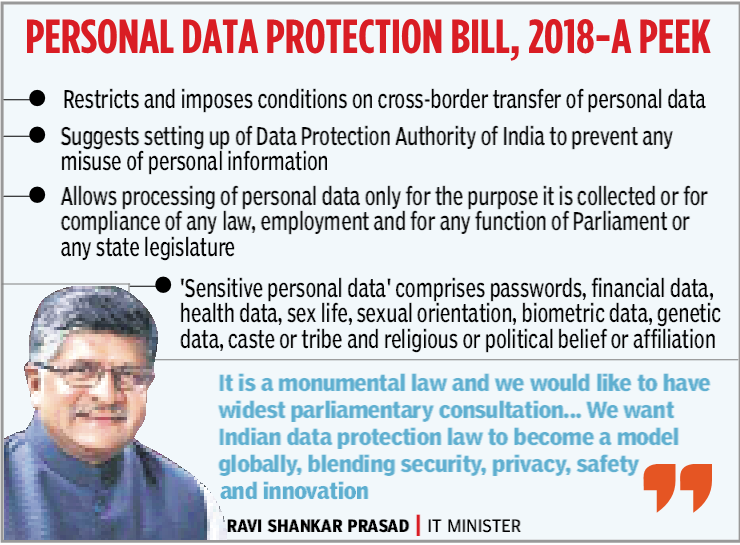
The draft of Personal Data Protection Bill, 2018 — which is based on the recommendations of the government-constituted high-level panel headed by Justice B N Srikrishna — restricts and imposes conditions on the cross-border transfer of personal data, and suggests setting up of Data Protection Authority of India to prevent any misuse of personal information.
The panel submitted its report on data protection as also the draft of the bill to the government Friday.
The draft provides for a penalty of `15 crore or 4 per cent of the total worldwide turnover of any data collection entity, including the state, for violation of personal data processing provisions.
Failure to take prompt action on a data security breach can attract up to `5 crore or 2 per cent of turnover, whichever is higher, as a penalty.
“The Bill provides that right to privacy is a fundamental right and it is necessary to protect personal data as an essential facet of informational privacy,” the draft said.
It allowed processing of personal data only for the purpose it is collected or for compliance of any law, employment and for any function of Parliament or any state legislature. ‘Sensitive personal data’ comprises passwords, financial data, health data, sex life, sexual orientation, biometric data, genetic data, caste or tribe and religious or political belief or affiliation.
According to the draft, personal data means “data about or relating to a natural person who is directly or indirectly identifiable, having regard to any characteristic, trait, attribute or any other feature of the identity of such natural person, or any combination of such features, or any combination of such features with any other information.”
“Personal data may be processed on the basis of the consent of the data principal, given no later than at the commencement of the processing,” it said, adding that processing of sensitive personal data should be on the basis of explicit consent. It provides for the processing of personal data only for purposes that are clear, specific and lawful. Collection of personal data has been limited to such data that is necessary for the purposes of processing.
Data fiduciary, which includes the state, has to give the individual information of the purpose for which the personal data is to be processed. It will retain personal data only as long as may be reasonably necessary to satisfy the purpose for which it is processed. It provides for the right to be forgotten after the particular purpose has been served.
The draft restricts cross-border transfer of personal data and gives exemption on use of personal data for national
security, crime investigation, legal
proceedings and certain journalistic
purpose.
Besides the Data Protection Authority of India to prevent any misuse of personal data, ensure compliance and promote awareness of data protection, it also provides for setting up of an Appellate Tribunal. Compensation has to be given to any person who has been wronged, it has suggested. The draft bill makes obtaining, transferring or selling of personal data in contravention as an offence.
It has stated that it is necessary to create a collective culture that fosters a free and fair digital economy, respecting the informational privacy of individuals, and ensuring empowerment, progress and innovation.
Headed by Justice B N Srikrishna, the panel handed the report to IT Minister Ravi Shankar Prasad, wrapping up nearly one year of deliberations.
Data Bill moots ‘explicit consent’
Right to privacy is a fundamental right and it is necessary to protect personal data as an essential facet of informational privacy